Obstetrics | Our Speciality
Our Speciality
The number of patients received by the department each year is about 80,000, and there are about 2,000 pregnant women each year, of which more than one-third are high-risk pregnant women. The hospital and the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology has passed annual assessment by the government to be the Mother-Baby Friendly Hospital and has always had an excellent evaluation based on its efforts to promote breast milk.

We are one of the few hospitals that have been deemed to be the third-level referral center for high-risk pregnancies in Central Taiwan. We have extensive experience in co-operation with other departments such as Pediatrics, Cardiology, Metabolism and Radiology. High-risk pregnancy refers to the risks borne by the mother and the fetus during pregnancy, which could potentially threaten or harm the fetal or maternal health. The commonly-seen diseases related to high-risk pregnancies may include: the heart disease, pregnancy-induced hypertension, diabetes mellitus, two or more pre-term births or consecutive miscarriages.
As for prenatal genetic diagnosis and ultrasound diagnosis for congenital defects, the department also has rather impressive outcomes. Although the number of people for reproduction is rapidly decreasing in the era of declining birth rate, we still continue to build the delivery room and purchase equipment to provide the best service for pregnant women.

In addition, the Department of Medical Genetics has a complete system for genetic disease diagnosis and treatment by offering inspection, counseling, diagnosis, and medical services for genetic diseases, prenatal examinations and congenital metabolic abnormalities. The purpose of prenatal genetic diagnosis is to predict fetal health and protect eugenic health.
The Department of Medical Genetics mainly utilizes the most advanced molecular medicine technology to accurately diagnose mutations or deficiencies in human genes from the premarital stage to the prenatal stage. 1) pre-marital health checkup and health consultation - as a reference for future fertility programs; 2) chorionic villus sampling or Amniocentesis for prenatal genetic diagnosis – to judge if the fetus contains any poor genes; 3) biochemical genetics and diagnosis of congenital metabolic diseases.
Details of prenatal diagnosis are set out as follows:

The hospital has a cytogenetic diagnosis room to provide services like blood screening, chromosomal abnormalities screening (including noninvasive fetal chromosomal testing), and ultrasonographic measurement of fetal neck zona pellucida thickness. We suggest high-risk groups undergo villus sampling or amniocentesis for further diagnosis, or the fetal ultrasound scan to rule out the possibility of congenital heart disease. In addition to the First-Trimester Down's Syndrome Screening, we also offer the Second-Trimester Down's Syndrome Screening. In amniocentesis, we can use the amniotic fluid to test genes on a chip to further grasp the fetus chromosomal defects or metabolic abnormalities.
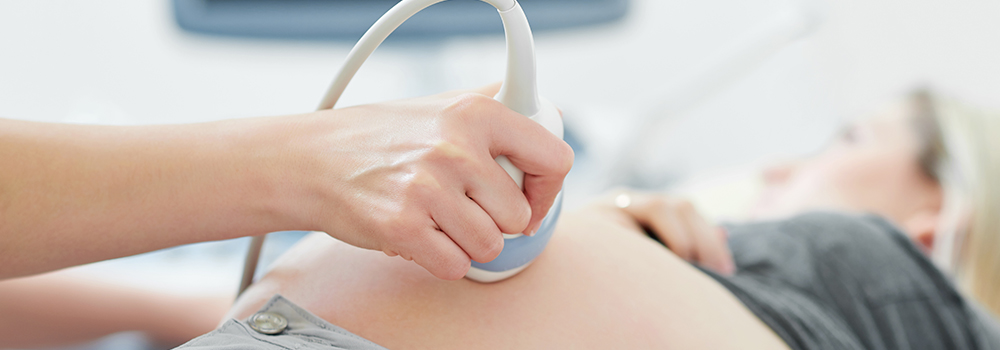
Ultrasound diagnosis can help detect the development of the fetus and structural abnormalities in a non-invasive way during the entire pregnancy period. In addition to the latest GE Voluson E10 ultrasonic machine that can help the diagnosis process, we also have an excellent diagnostic team. The ultrasound examination for about 20 weeks is offered based on health care. Although technicians are there to operate the ultrasound examination, but they have received the high-level ultrasound training to do the preliminary screening for pregnant women. The high-level ultrasound examination will be operated by doctors, and more emphasis will be put on the central nervous system and cardiovascular disease diagnosis. In this department, we also provide follow-up tracking services for 32 weeks, which mainly focus on the examination of important organs, and feto-placental function measurement.

For the screening of abnormal fetuses, we can provide intrauterine invasive treatment. For example, for fetuses with severe anemia, we can use intrauterine blood transfusion to improve their heart function. In the face of more and more cases of multiple pregnancies, we also provide the embryo reduction technique to reduce the risk that pregnant women continue to face during their pregnancies. And even if the fetus has ascites or pleural effusion that may affect the development of their organs, we can also carry out the water chamber suction therapy to improve the prognosis of the fetus.
