Acute Myocardial Infarction Detection Software
About CMUH
Acute Myocardial Infarction Detection Software
Product Overview
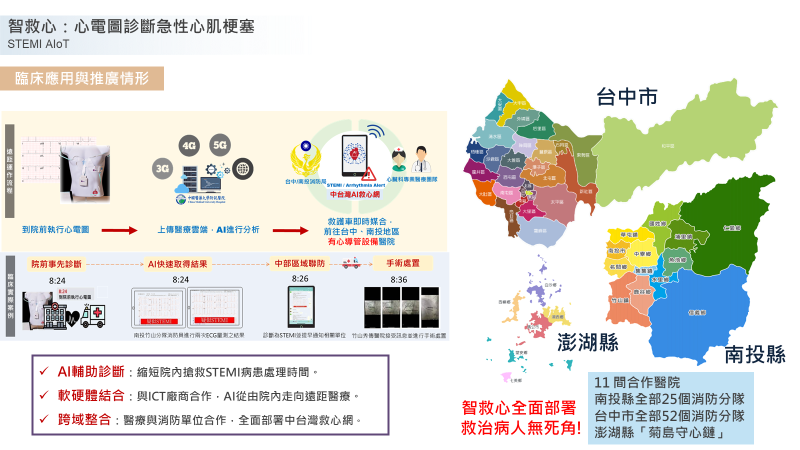
ST‑elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) is one of the most critical cardiovascular emergencies. Without timely diagnosis and reperfusion, patients may suffer permanent myocardial damage leading to fatal arrhythmias, cardiogenic shock, ventricular rupture, or cardiac tamponade. To reduce such complications and improve clinical outcomes, the door‑to‑balloon time (D2B) in primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PPCI) must be shortened. To accelerate D2B, we implemented a 24‑hour AI‑based triage system that combines AI‑assisted ECG interpretation for STEMI with the ASAP clinical risk score, rapidly identifying high‑risk patients who require prompt ECG examination.
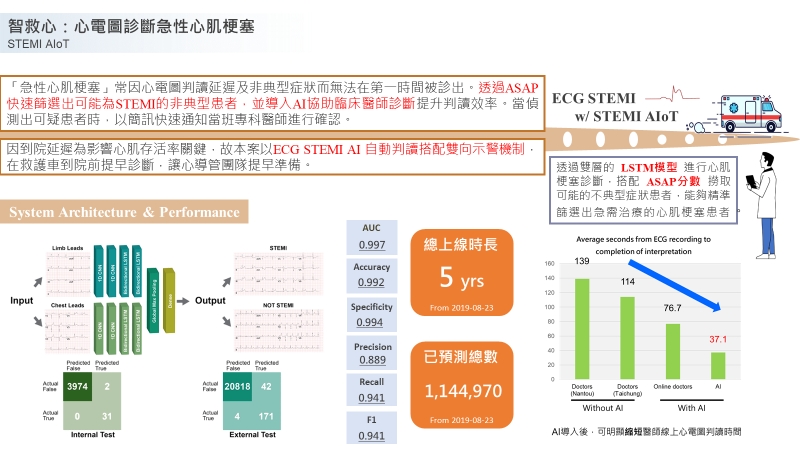
The AI triage system integrates a convolutional neural network (CNN) with long short‑term memory (LSTM) to detect STEMI on ECGs and uses the ASAP score to prioritize patients. The model was developed on 2,907 twelve‑lead ECGs, including 882 STEMI and 2,025 non‑STEMI cases.
During the trial phase, 154 STEMI patients were enrolled—68 after AI triage implementation and 86 under the traditional workflow. Compared with the traditional group, the AI group’s mean D2B time was significantly reduced from 64.5 ± 35.3 min to 53.2 ± 12.7 min (P = 0.0071); 98.5 % achieved D2B < 90 min. Among patients with an ASAP score ≥ 3, the median door‑to‑ECG time dropped from 30 min (IQR 7–59) to 6 min (IQR 4–30, P < 0.001). On 21,035 emergency ECGs, the model achieved overall metrics of accuracy 0.997, precision 0.802, recall 0.977, AUROC 0.999, F1 0.881, and specificity 0.998.
Implementing this round‑the‑clock AI triage system markedly shortened D2B time—especially during nights and holidays—and increased the proportion of cases meeting the 90‑minute benchmark. Without adding staff, the system improves efficiency in delivering PPCI to STEMI patients and merits widespread adoption.
Videos
Emergency AMI Platform
Central Taiwan Heart‑Saving Network
Related Publications (with Explainability Analyses)
| Title | Journal | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Usefulness of multi‑labelling artificial intelligence in detecting rhythm disorders and acute ST‑elevation myocardial infarction on 12‑lead electrocardiogram | European Heart Journal | 2021 |
| Usefulness of Machine Learning‑Based Detection and Classification of Cardiac Arrhythmias With 12‑Lead Electrocardiograms | Canadian Journal of Cardiology | 2021 |
| Implementation of an All‑Day Artificial Intelligence‑Based Triage System to Accelerate Door‑to‑Balloon Times | Mayo Clinic Proceedings | 2022 |
| Artificial intelligence‑assisted remote detection of ST‑elevation myocardial infarction using a mini‑12‑lead electrocardiogram device in prehospital ambulance care | Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine | 2022 |
Media Coverage
| Date | Source | Headline |
|---|---|---|
| 2021‑11‑26 | Hospital Website | “Central Taiwan AI Heart‑Saving Network” Prehospital STEMI Remote Diagnosis Races Against Time |
| 2021‑04‑30 | Hospital Website | STEMI ECG Diagnosis Platform Improves Rural Care Before Hospital Arrival |
| 2021‑04‑28 | China Times | Ambulance AI ECG Diagnoses STEMI En Route |
| 2020‑10‑21 | CTS News | AI Identifies Atypical STEMI in Patient With Abdominal Pain |
| 2020‑10‑21 | Liberty Times | Persistent Abdominal Pain Revealed as STEMI—AI in ED Detects Early and Saves a Life |
| 2020‑10‑21 | Asia Pacific News | AI Rescues STEMI—Timely and Effective Treatment With AI Assistance |
| 2020‑10‑21 | Online Community News | AI‑Assisted STEMI Interpretation Cuts Rescue Time—Sets National Record of 32‑Minute Revascularization |